RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks
- Key idea is redundancy
- Why?
RAID Types
- Hardware - physical hardware controls RAID
- More expensive
- array is presented as a single logical disk to OS
- manage with tools provided by vendor
- Cannot nest raid levels
- hope your raid card never dies
- may have better performance over software RAID for very large arrays
RAID Types
- Software - kernel takes care of RAID functionality
- OS has to take physical disks and convert to logical
- can use any regular block device (paritition, disk, files…)
- supports RAID nesting (create a RAID 0 of RAID 6)
- tool: mdadm (supports hot spares, hot swap)
- Why not? If you have to dual boot.
RAID Types
- Fake - Essentially software raid, provided by the BIOS on the mobo.
- different from vendor to vendor
- tool: dmraid
- usually only supports RAIDing an entire disk, not partitions
- lose mobo, lose data
- usually only used when dual-booting (win and linux)
RAID Types - Fake raid again
The terms “Fake RAID” or “BIOS RAID” denote systems with no RAID controller, but with a simple BIOS that is able to do basic RAID operations on an array of disks. For the actual runtime RAID implementation, this RAID solution relies on a OS driver. On Windows this will usually be a driver from the RAID vendor.
Typically more useful for Windows as linux software raid works pretty well.
RAID Levels
There are too many RAID levels that exist. But, we will go over the MOST common ones that you will see in the wild (and the ones supported on our machines):
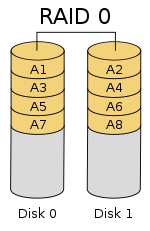
RAID 0 - Striping
Makes multiple disks look as if they were a single disk.
Advantages:
- You get more disk space
- Speed?
Disadvantages:
- No redundancy
- LVM Is better
RAID 0 - Striping
RAID 1 - Mirroring
Data blocks are duplicated to another physical disk.
Advantage:
Dis:
- Two write operations have to occur per block
RAID 1 - Mirroring

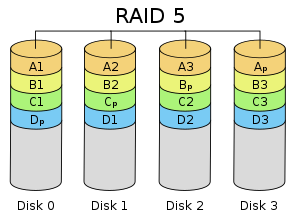
RAID 5 - Parity
Blocks are alternately written to different disks. A parity block is also written. Must have at least 3 disks
RAID 5 - Parity
RAID 10

RAID
See table 11-3 here
Managing RAID
Hardware manufacturers can provide utilities to configure hardware raid. Some commands are also available in the kernel:
- mdadm (for software/fake raid)
- dmraid (for software/fake raid)
- understands more metadata formats
cat /proc/mdstat
Mdadm how to
See my cheatsheet
This site might also be useful.
Misc
Raid chunk size - The default when creating an array is 512KB (using mdadm)
- If you choose a chunk size of 64K, a 256K file will use 4 chunks. (If this were raid 0 with 4 drives, this would work nicely)
- What if you had a chunks size of 256K? You’d only use 1 chunk, and the benefits of striping would be negligible.




